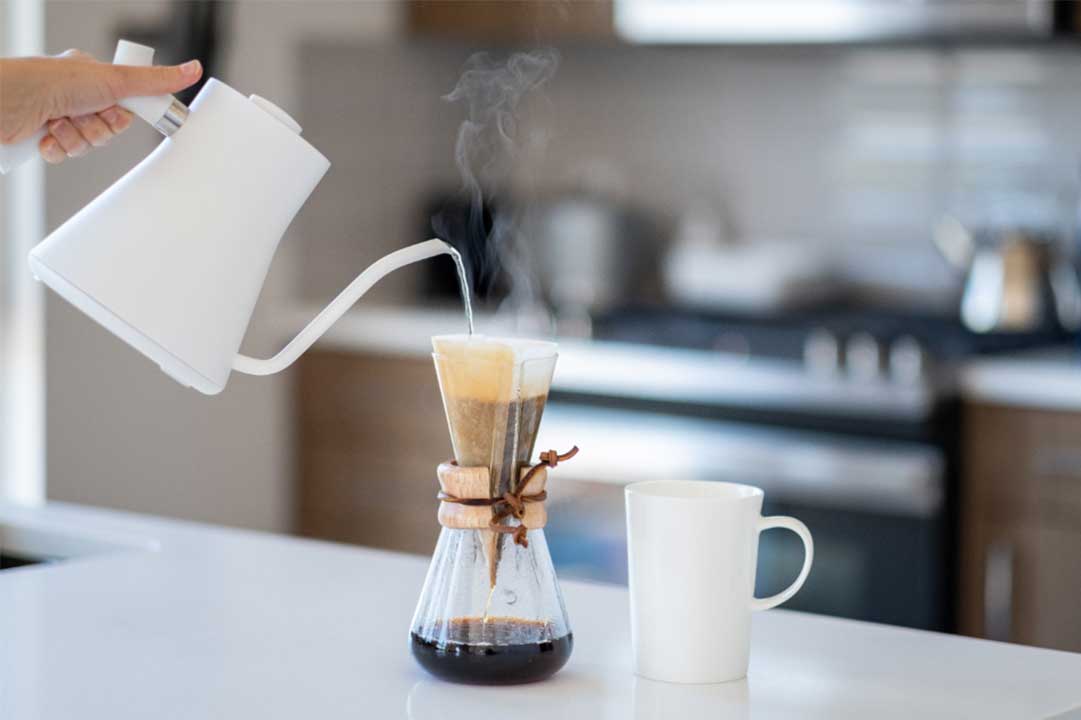
The brewing process of coffee is significantly influenced by the quality and properties of water. The characteristics of water play a crucial role in determining the flavor profile of coffee. Here are the fundamental effects of water on coffee brewing and the characteristics from which these effects originate:
- Mineral Content:
The minerals present in water are a crucial factor that affects the taste of coffee. Ideal water should have a balanced mineral content. Minerals such as phosphorus, magnesium, and calcium can enhance the flavor of coffee. However, excessive mineral content can spoil the taste of coffee and lead to the formation of unwanted sediment.
- Acidic and Basic Properties:
The pH level of water determines whether coffee exhibits acidic or basic properties. Acidic water emphasizes the bright acidity and fruity flavors of coffee. On the other hand, basic water can create a coffee profile with lower acidity. The optimal pH level is generally below 7, but the preferred pH may vary depending on the type of coffee and individual preferences.
- Temperature:
The temperature of water influences the rate at which soluble compounds are extracted during the coffee brewing process. Hot water is crucial for extracting flavor and aroma from coffee beans. However, excessively hot water can result in a bitter or burnt taste. The optimal temperature usually falls within the range of 90-96°C, providing a suitable brewing environment for various types of coffee.
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Content:
The presence of oxygen in water can assist in extracting aromatic compounds from coffee beans. However, excessive exposure to oxygen can lead to rapid oxidation of fresh coffee. Carbon dioxide, a gas released by coffee beans, can introduce unwanted flavors during the brewing process. Therefore, careful control of the oxygen and carbon dioxide content in water is essential.
- Water-Coffee Interaction:
The interaction between water and coffee beans forms the foundation of the brewing process. The duration of water contact with the beans determines the quantity and type of soluble compounds extracted. This interaction defines the body, acidity, and flavor profile of coffee. Achieving optimal water-coffee interaction requires careful control of the brewing process and adjustment of the water-coffee ratio.
In conclusion, water in the coffee brewing process is a complex system where various factors come together. Characteristics such as water quality, mineral content, pH level, temperature, and gas content determine the final flavor profile of coffee. Coffee enthusiasts and brewers can achieve their desired coffee experience by carefully balancing these characteristics.